How To Set Up PostgreSQL 17 on Docker CE

On this tutorial, we will show you how to set up PostgreSQL database engine on Docker Community Edition (CE). As we know, if PostgreSQL is a powerful open-source relational database. Running it inside a Docker container allows for easy setup, isolation, and management. This guide will walk you through installing and setting up PostgreSQL on Docker.
Prerequisites
- Docker installed on your system. If not, install it from Docker’s official website.
- Basic knowledge of Docker commands.
Docker installation on Ubuntu 24.04 has been covered on How To Install Docker CE on Ubuntu 24.04 LTS article.
Setting Up PostgreSQL on Docker
To set up PostgreSQL database engine on Docker will be consist of several tasks as summarize below :
Step 1: Pull the PostgreSQL Docker Image
Step 2: Run a PostgreSQL Container
Step 3: Verify the Running Container
Step 4: Access the PostgreSQL Database
Step 5: Persisting Data Using a Volume (Optional)
Step 7: Stopping and Removing the Container
Details explanation of each step will be covered on following sub sections.
Step 1: Pull the PostgreSQL Docker Image
We need to get the latest PostgreSQL image which will be used on our tutorial. To get the latest PostgreSQL image from Docker Hub, run:
docker pull postgres
Or if we need other version of PostgreSQL, we just submit the command :
docker pull postgres:<main_version>
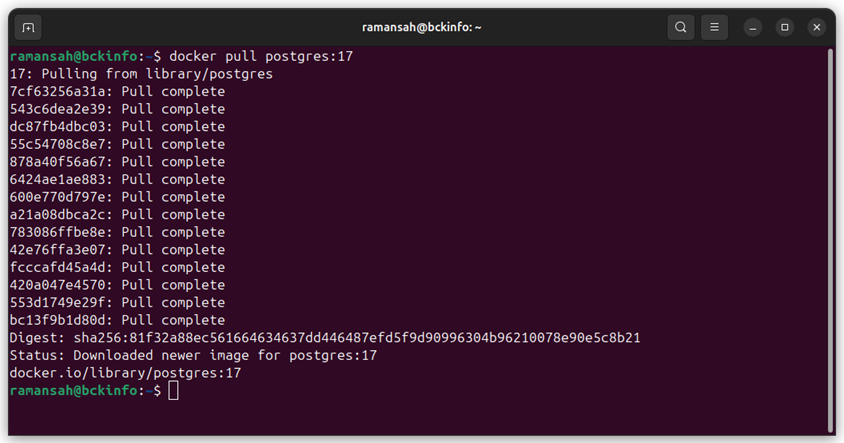
On this tutorial, since we know that the latest version of PostgresQL is version 17, then we will submit the following command :
docker pull postgres:17
The output will be as shown below :
ramansah@bckinfo:~$ docker pull postgres:17 17: Pulling from library/postgres 7cf63256a31a: Pull complete 543c6dea2e39: Pull complete dc87fb4dbc03: Pull complete 55c54708c8e7: Pull complete 878a40f56a67: Pull complete 6424ae1ae883: Pull complete 600e770d797e: Pull complete a21a08dbca2c: Pull complete 783086ffbe8e: Pull complete 42e76ffa3e07: Pull complete fcccafd45a4d: Pull complete 420a047e4570: Pull complete 553d1749e29f: Pull complete bc13f9b1d80d: Pull complete Digest: sha256:81f32a88ec561664634637dd446487efd5f9d90996304b96210078e90e5c8b21 Status: Downloaded newer image for postgres:17 docker.io/library/postgres:17
Step 2: Run a PostgreSQL Container
After pulling the PostgreSQL container, then we will run it on the system. Use the following command to run a PostgreSQL container:
docker run --name docker_bckinfo -e POSTGRES_USER=admin -e POSTGRES_PASSWORD=bckinfo123 -e POSTGRES_DB=bckinfodb -p 5444:5444 -d postgres
Explanation of the Flags:
--name docker_bckinfo→ Assigns a name to the container.-e POSTGRES_USER=admin→ Sets the database user.-e POSTGRES_PASSWORD=bckinfo123→ Sets the database password.-e POSTGRES_DB=bckinfodb → Creates a default database.-p 5444:5444→ Maps the PostgreSQL port to the local machine, default port is : 5432.-d postgres→ Runs the container in detached mode.
Otput will be as shown below :
ramansah@bckinfo:~$ docker run --name docker_bckinfo -e POSTGRES_USER=admin -e POSTGRES_PASSWORD=bckinfo123 -e POSTGRES_DB=bckinfodb -p 5444:5444 -d postgres 6c199053efa2d405ba89dd99068d2267c701ba435feebea924874ccdeda365de
Step 3: Verify the Running Container
Check if the container is running, by using command line :
docker ps
the output will be as shown below :
ramansah@bckinfo:~$ docker ps CONTAINER ID IMAGE COMMAND CREATED STATUS PORTS NAMES 6c199053efa2 postgres "docker-entrypoint.s…" 37 seconds ago Up 36 seconds 5432/tcp, 0.0.0.0:5444->5444/tcp, [::]:5444->5444/tcp docker_bckinfo
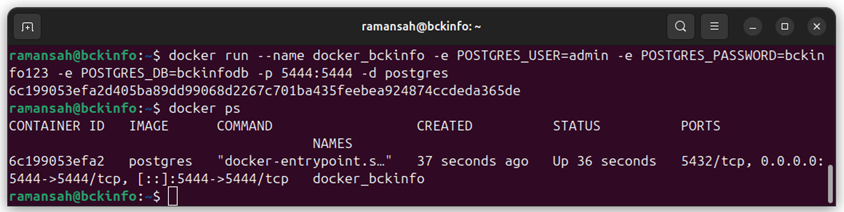
The PostgreSQL container has already run.
Step 4: Access the PostgreSQL Database
On this stage, we will access PostgreSQL shell inside the running container. For this purpose we will submit command line :
docker exec -it docker_bckinfo psql -U admin -d bckinfodb
The output will be as shown below :

On this step, we just logged in ot bckinfodb database on PostgreSQL hosted on Docker.
Step 5: Persisting Data Using a Volume (Optional)
By default, data inside a container is lost when the container is removed. To persist data, use a Docker volume:
docker run --name docker_bckinfo -e POSTGRES_USER=admin -e POSTGRES_PASSWORD=mypassword -e POSTGRES_DB=bckinfodb -p 5444:5444 -v pgdata:/var/lib/postgresql/data -d postgres
Step 6: Stopping and Removing the Container
On this stage, we will To stop and remove PostgreSQL container:
1. Stoping the PostgreSQL container
docker stop docker_bckinfo
2. Removing PostgreSQL container
docker rm docker_bckinfo

Conclusion
By following these steps, you have successfully set up PostgreSQL on Docker. You can now use it for development, testing, or production environments with ease.